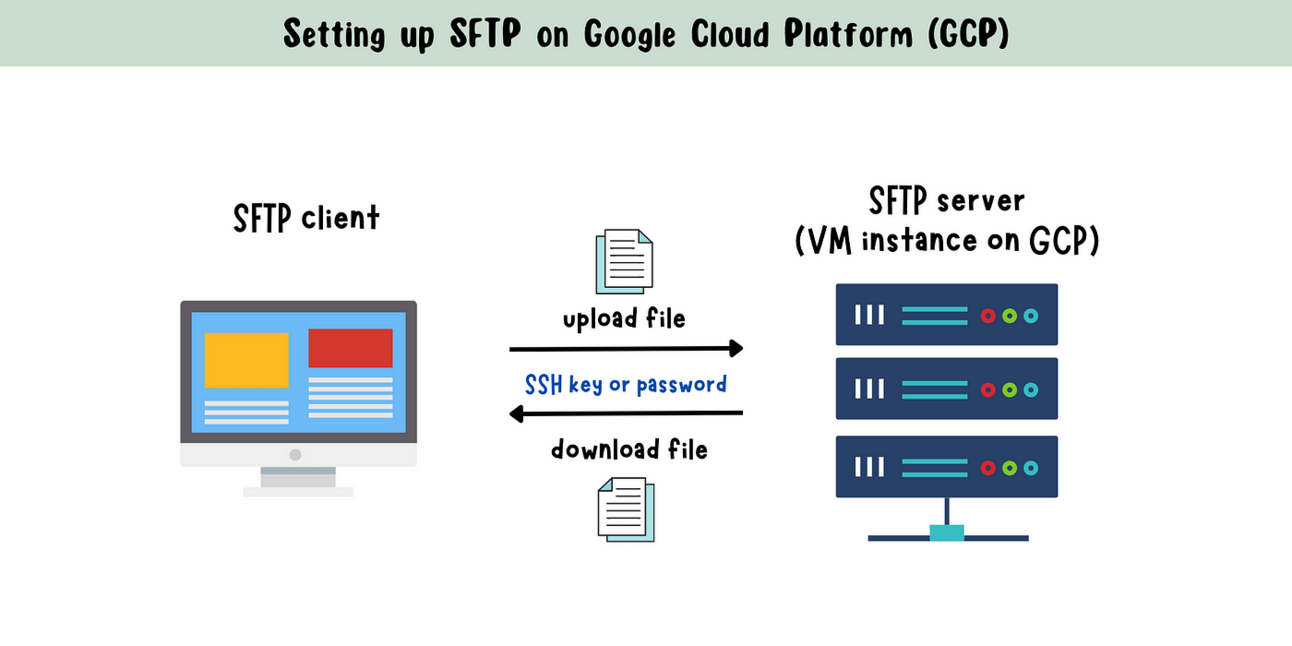
Creation of an SFTP Server on GCP and Connecting via SFTP
Introduction: In today's digital landscape, secure and efficient file sharing is a fundamental requirement for individuals and businesses. Creating an SFTP (Secure File Transfer Protocol) server on Google Cloud Platform (GCP) offers a reliable and secure solution for transferring files, ensuring data integrity, and maintaining a seamless workflow. This guide provides step-by-step instructions to help you set up an SFTP server on GCP, enabling you to establish secure connections and effortlessly exchange files with enhanced peace of mind.
Prerequisites: Before getting started, ensure you have the following prerequisites:
A Google Cloud Platform (GCP) account with sufficient permissions to create a VM instance and manage networking resources.
An SFTP client software such as FileZilla or WinSCP installed on your local machine.
Implementation Steps:
Step 1: Create a GCP VM Instance:
Log in to your GCP Console (https://console.cloud.google.com/).
Navigate to the Compute Engine section.
Click on "Create Instance" to create a new VM instance.
Provide a name for the instance (e.g., "sftp-server").
Choose the desired region and zone.
Select the machine type based on your requirements (e.g., Ubuntu).
Under "Boot disk," select an operating system image (e.g., Ubuntu 22.04 LTS) and set the desired disk size.
Enable the "Allow HTTPS traffic" option.
Click "Create" to create the VM instance.
Step 2: Install OpenSSH Server:
Once the VM instance is created, click on the SSH button next to the instance name to open an SSH session to the VM. This will install the OpenSSH server and start it automatically.
Run the following commands in the SSH session:
sudo apt-get update
sudo apt-get install openssh-server -yStep 3: Create an SFTP User
Create an SFTP group by running the command:
sudo groupadd sftpusersCreate an SFTP user (e.g., "usera") and add them to the SFTP group, set password and create a home directory for the user:
sudo useradd -g sftpusers -d /home/{username} -s /bin/false {username}
sudo passwd {username}
sudo mkdir /home/{username} (do not chmod 777)Step 4: Generate SSH Key Pair:
Open the command prompt or terminal on your local machine.
Generate an SSH key pair using the following command:
ssh-keygen -t rsa -b 4096 -C "[email protected]"Enter a secure passphrase when prompted (optional but recommended).
Step 5: Add SSH Public Key to SFTP Server
Log in to your GCP VM instance via SSH using the GCP Console or a terminal:
ssh username@your_server_ipCreate a directory named .ssh in the user's home directory (if it doesn't exist) and execute following commands:
mkdir ~/.ssh
nano ~/.ssh/authorized_keys
chmod 700 ~/.ssh
chmod 600 ~/.ssh/authorized_keysPaste your public ssh-key in this file, save & exit. (Press Ctrl+O and give yes, Ctrl+X to exit)
ORAlternatively, Upload SSH Keys to VM Instance:
In the GCP Console, navigate to the Compute Engine section and then to Settings Metadata.
Add your SSH public key to the "SSH keys" section. Make sure to use the correct format for your SSH key.
Restart the OpenSSH server to apply the changes:
sudo service ssh restartStep 6: Configure OpenSSH Server on GCP VM:
Verify that the SSH server is running, If the SSH server is not running, start it:
sudo service ssh status
sudo service ssh startVerify that the SSH server is running, If the SSH server is not running, start it:
sudo nano /etc/ssh/sshd_configFind the line that says “Subsystem sftp /usr/lib/openssh/sftp-server” and replace it with the following:
Subsystem sftp internal-sftp
Match group sftpusers
ChrootDirectory %h
X11Forwarding no
AllowTcpForwarding no
ForceCommand internal-sftpThis will configure OpenSSH to use the internal-sftp subsystem for SFTP, restrict SFTP access to the SFTP users group, chroot each user to their home directory, and prevent SSH and TCP forwarding.
To use ssh keys for authentication:
PubkeyAuthentication yes
PubkeyAcceptedAlgorithms +ssh-rsa,ssh-ed25519
AuthorizedKeysFile .ssh/authorized_keys .ssh/authorized_keys2
# To disable tunneled clear text passwords, change to no here!
PasswordAuthentication noSave the file and exit. (Press Ctrl+O and give yes, Ctrl+X to exit)
NOTE: If you want to create users and connect using username/password then write as yes instead of no in PasswordAuthentication in above section, also search for PasswordAuthentication duplicates in sshd_config and set it to yes.
Restart the SSH server to apply the changes:
sudo systemctl restart ssh
Step 7: Connect to GCP VM via SFTP:
Open FileZilla (or any SFTP client software) on your local machine.
Connect to the SFTP server using the VM instance's public IP address, SFTP username (the one used during SSH login), and the private key matching the uploaded public key.
If you want to login using username & password in logon type select “Ask for password”.
(Make sure you set PasswordAuthentication to yes in sshd_config file) refer step 4.Once connected, you can navigate to the appropriate directory on the server and transfer files securely via SFTP.

Step 8: Create a directory and set the necessary permissions in sftp-server in GCP:
mkdir /home/username/uploads
sudo chmod u+w /home/username/uploadsStep 9: Share files via SFTP from your local to sftp-server in GCP using Filezilla:
Drag and drop a file “abc.txt” from your local to /home/username/uploads folder in sftp-server.
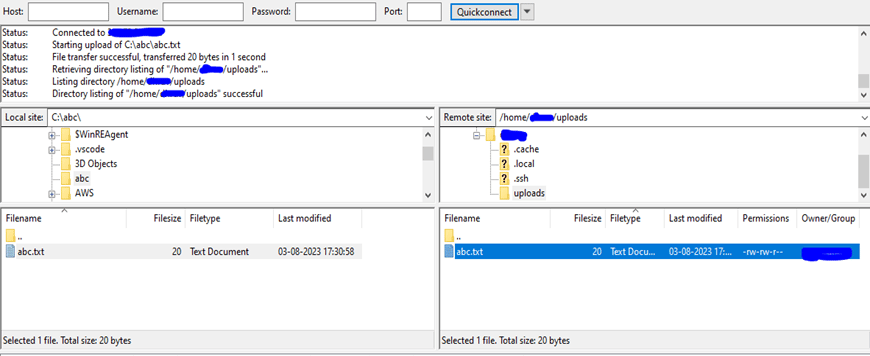
Step 10: Verify file shared from your local to sftp-server in GCP server:
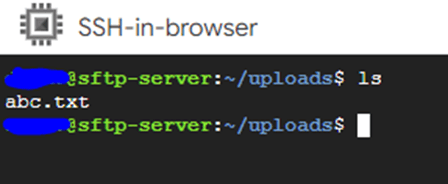
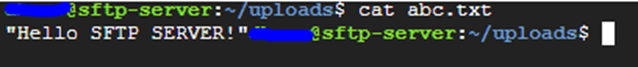
That’s it! You have now successfully shared a file via SFTP from local to server in GCP.
Troubleshooting: If you encounter the "Permission denied (publickey)" error while connecting via SSH or SFTP, follow these troubleshooting steps:
Check the permissions of your private key file (
id_rsa) on your local machine. It should have restricted access only for your user. Use the following command to set the correct permissions:chmod 600 /path/to/private_key_fileIf the issue persists, check the
known_hostsfile on your local machine (usually located in~/.ssh/known_hosts). Sometimes, old or incorrect host keys can cause issues. To resolve this, remove the entry for your VM's IP address from theknown_hostsfile.
Conclusion: Congratulations! You have successfully created an SFTP server on Google Cloud Platform (GCP) and connected to it securely using SFTP protocol. By following the steps outlined in this blog post, you can streamline the process of setting up SFTP servers on GCP and easily transfer files securely. Additionally, the troubleshooting steps provided will help you handle common issues and ensure a smooth SFTP experience. Happy file sharing on your new SFTP server!
